Why SSL? You may have noticed that some website’s URL starts with “http://” whereas many URLs start with “https://”—an addition of ‘s’ may seem small but carries a bigger purpose. The presence of ‘s’ in the URL means the website is secure and encrypted, and any data that you give to the website is only shared with the website and is completely safe. The ‘s’ present is known as Secure Sockets Layer, otherwise called SSL. If you are a marketer it is important that your website has SSL security as a consumer always looks for SSL certificates when he shares important information like credit card details to pay or purchase. Today, the presence of SSL is not a choice but has become a basic necessity of websites. This article will cover everything about SSL like What is an SSL certificate and more importantly, the importance of SSL. Other than only educating you about SSL it will also help you get free SSL certificates using letsencrypt.
There are tons of SSL certificates that exist where some are free, some are cheap, and some are very, very expensive (almost 4000.00USD /year).
This does not mean that free or cheap SSL certification is not worthy.
They are! As some online marketers like Let’s encrypt (https://letsencrypt.org/) understand the necessity it holds and offers free certificates and manage their funding through donations; in fact, they have offered over one billion free SSL certificates as of now.
The expensive ones exist because they offer high-security privileges which could not be handed-out free.
Do you want to know why some SSL certificates are free, some cheap, and why some are expensive? Well, you can understand this by understanding SSL and how they work.
Table of Contents
What is an SSL certificate?
SSL, well, the Secure Socket Layer which is the standard security technology that establishes an encrypted link between a server and a browser—this secret encryption ensures that whatever the data is shared from a browser to a web server or vice-versa is hidden.
See, the SSL has two central objectives—the encryption and the identification.
- Encryption
The encryption is the part where computers hide what is sent to the other computer. It does by changing the content, for example, speaking in code as spies do. Obviously, it is much more complex than that but you get the idea, right! Consider this— If you share a piece of information like your credit card details without encryption with the website from where you want to purchase. These details can be easily intercepted by a third-party who may have an interest in your money. But with encryption, the information you will share will be garbage to others. It is done as:
- Your computer and server agree on how to encrypt
- The Web Server Sends Certificate
- Your computer says “Start Encrypting”
- Server agrees
- And, your details and message get encrypted—which will be trash to anyone other than the two computers that are communicating
- Identification
The identification makes sure that the computer you are speaking to is the one you trust. For example, how can you trust the computer you are speaking?
This is important as SSL will encrypt the message but how you do know that you are sharing the information with the computer that you want—it can be agreed by some other computer. This works like:
- The web server asks the Certification Authority for a certificate
- The certification authority creates a certificate after verifying the details of the company and signs it(cryptographically)
- This certificate will be installed in the server
- And, when a browser wants to communicate with your server it is issued with a root certificate(which may be correctly signed or be malicious)
- The browser, however, will only trust the correctly signed certificate
The details asked by the CA are a whole lot like where the server is located and what is the company, etc., and issues a certificate only when it completely authenticates the server. The secret key will change all the information like version, serial number, the algorithm, Validity, etc.
That’s all there to it—however, the importance of SSL is that the consumer can double click on the padlock and see the URL as https:// and feel safe that the information they are sharing with you is safe and secure.
Let’s go further.
Types of certificates
These certification authorities further categorize the certificate based on the level of validation and encryption which is further based on the number of domains and subdomains that will be under a single certificate.
- Extended Validation (EV SSL) —the most expensive ones.
- Organization Validated (OV SSL) Certificate—cheaper but almost the same as EV
- Domain Validation (DV) Certificate—easily certified and are for one domain.
- Wildcard SSL Certificates—you can use for subdomains.
- Unified Communications (UCC) SSL Certificate—multiple domains.
- Single Domain SSL Certificate—for one domain only.
How to get an SSL security?
After you figure out which SSL certificate you need—for example, if you are hosting on many platforms it means that you have separate domains and subdomains, and you need a different certificate than the website which controls only one domain.
If you have only one domain it means that the standard certificate is enough. As mentioned earlier, the cost of each of these certificates varies, some are cheap, some are expensive whereas some are free.
Yeah, like stated, letsencrypt is a Certification Authority which issues the certificate for completely free. However, they only give the certificate for ninety days, but upon the expiry date or prior to it (letsencrypt suggests every 60 days) you can manually renew the certificate. This is to stop the damages of key compromises and mis-issuance.
Free SSL certificates
- Let’sencrypt
The traditional CA will offer you a form—and filling it—you can get your certificate. However, letsencrypt does not provide you with that option. The usual way to get an SSL certificate from letsencrypt is that you download the software and follow the instruction attached, however, you should know that it involves being technical—coding and stuff. This link will help you through this method.
However, there are some third-party apps that you can use to get the certificate—the same way you get one from paid certificate providers. I’ll discuss this one—it’s completely safe but if you want to do the usual way you can proceed with the above link.
How to get an SSL certificate from letsencrypt?
I am going to use a third-party app to get the free SSL certificate from letsencrypt without going with the hassling of coding.
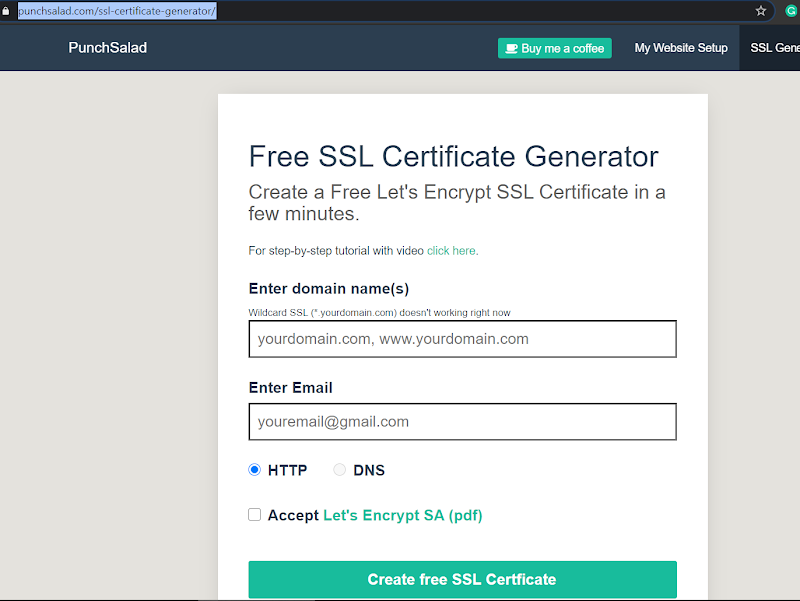
Enter your domain.com, and then www.your domain.com, and then email address for example:
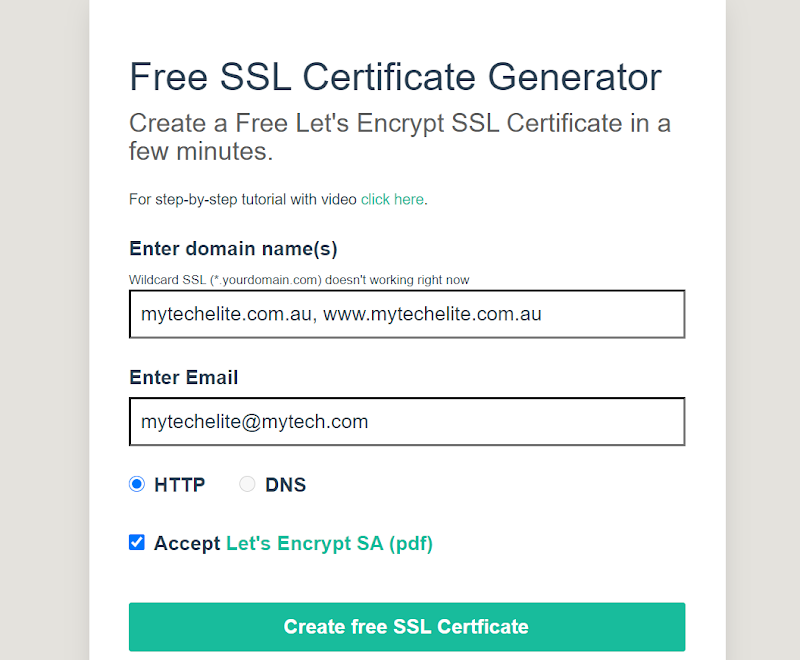
You can add your other subdomain subsequently following www.subdomain.com—note that—if you have a lot of subdomains, instead of writing www.yourdomain.com, write *.yourdomain.com.
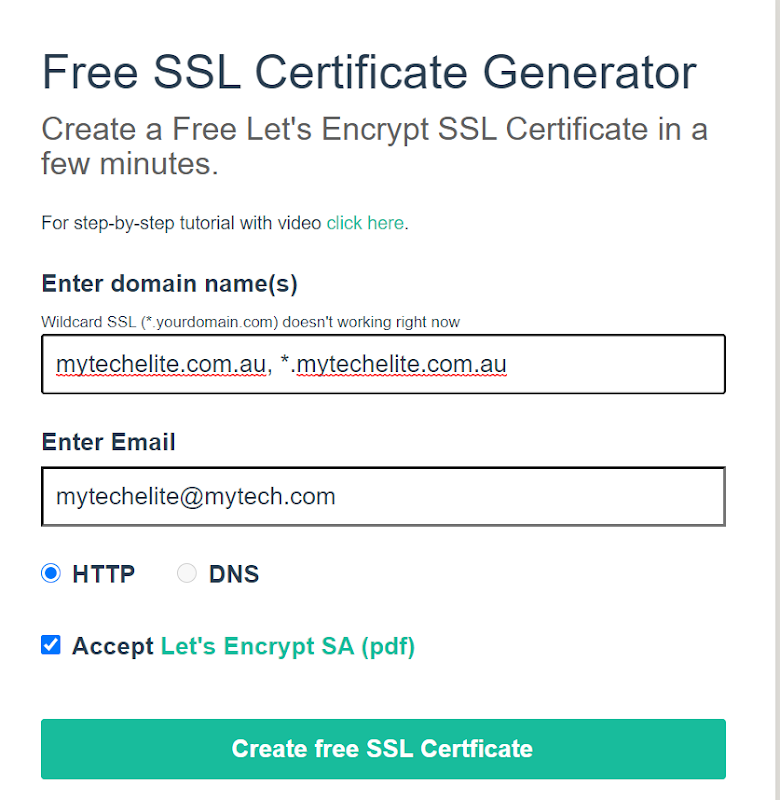
Also, if you want the wildcard—you have to move forward with DNS instead of HTTP chosen above—that method is different and a topic for some other time.
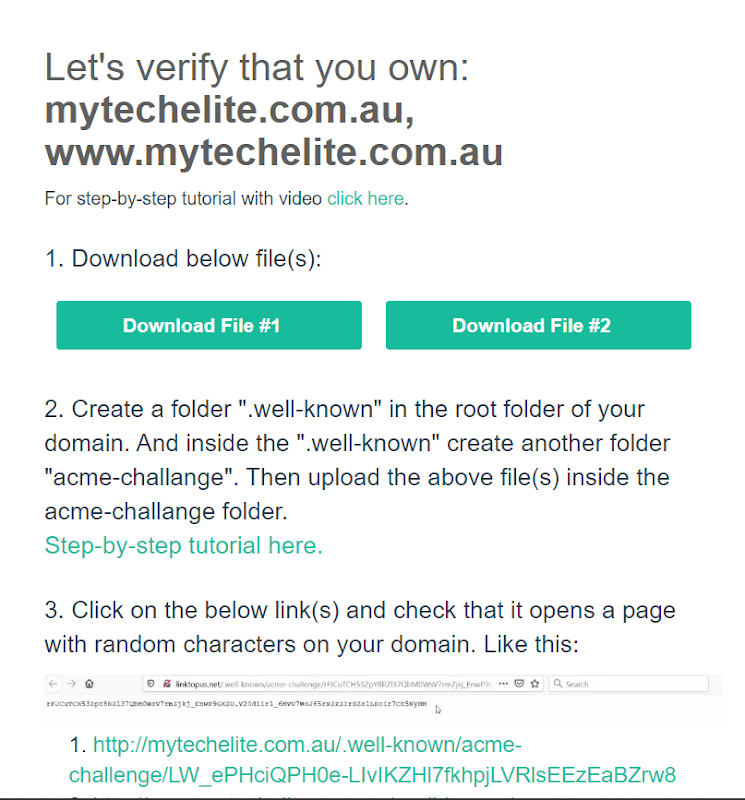
- When you click on the Create free SSL certificate—you will get two files which you have to download. After downloading, do not close this tab.
- After downloading the file, sign-in to your GoDaddy account and open the cPanel.
Note that—almost every cPanel has the same procedures, so even if you are not using GoDaddy, and have registered with any other domain providers. You can still proceed as the process is the same for almost every domain provider.
- After you log-in, select the ‘Manage’ option on the Web Hosting column.
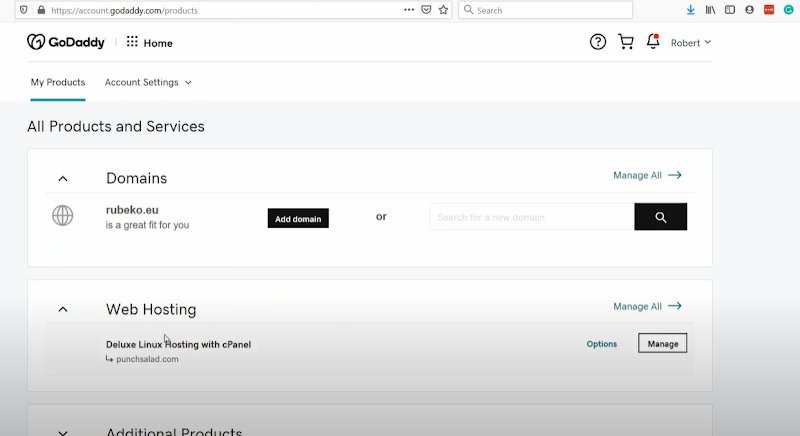
- On the redirected page, select cPanel admin.
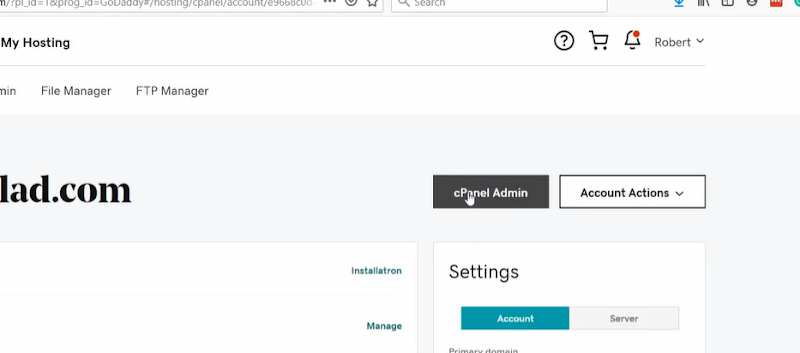
If you are using Managed WordPress—you will not have the option of cPanel, in this case, you have to use the https://www.cloudflare.com/.
5. Select the first option: File Manager
Under which select the public_html and if you have hidden files. Go to settings in the right uppermost corner and uncheck the option of hidden files.
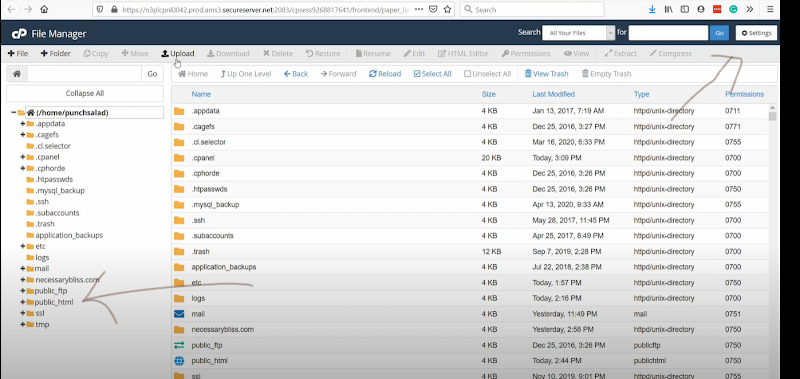
5. Now, go to your domain—here I am proceeding with one of the addon domain linkopus.net.
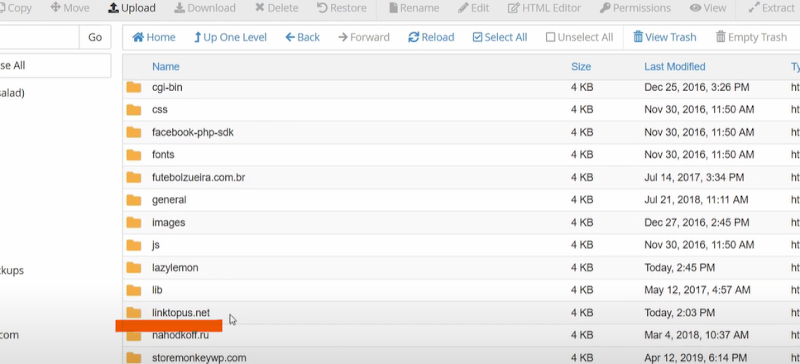
- Selecting which you have to create a folder with the name ‘.well-known’ : the folder has to be in this format, otherwise, it will not work.
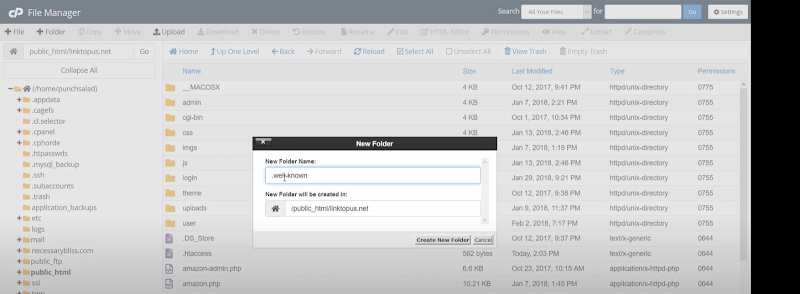
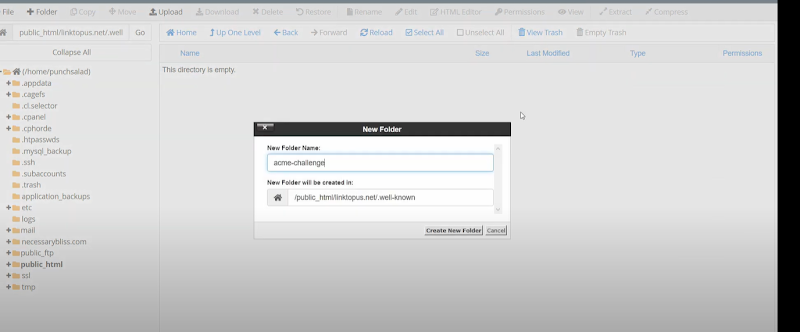
- Double-clicking the newly created .well-known folder you have to further create an additional folder named: ‘acme-challenge’.
- After you have created the folder—you have to upload the two files which you have downloaded earlier from punchsalad.
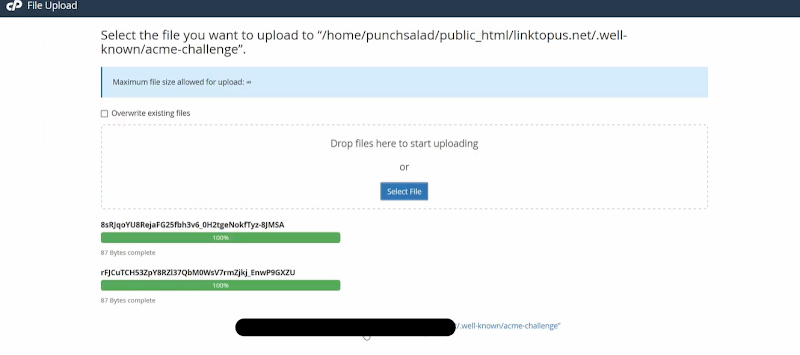
You can delete the files from your computer—as you do not have the use of it for the next 90 days.
- After you have done this—go back to the tab of punchsalad and click on both links given.
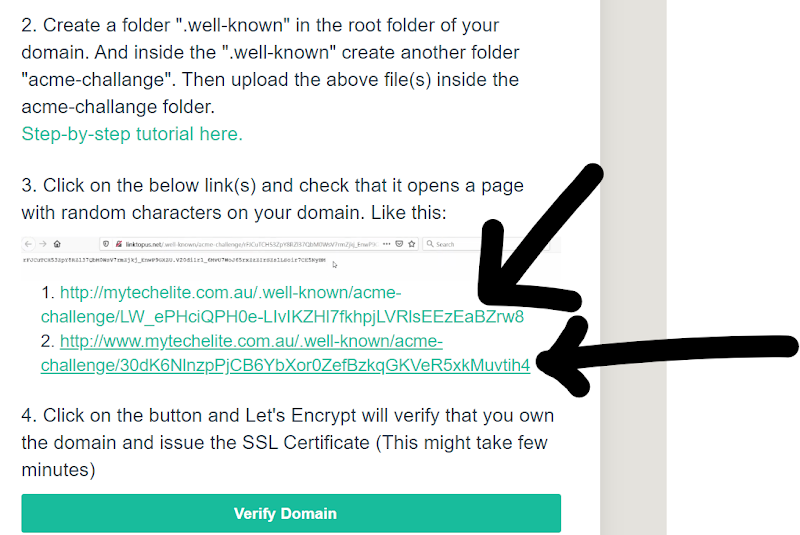
After clicking —you will see something like this, it means that the links are working.
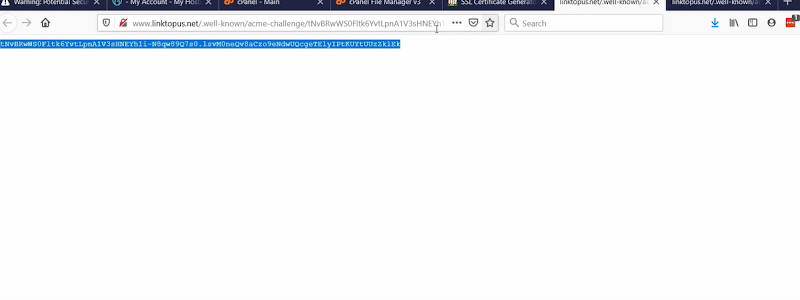
If you get an Error saying 404: Page Not Found.
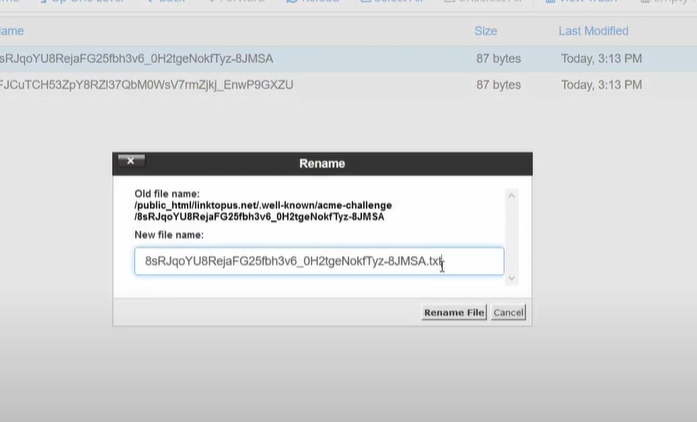
Just go back to the cPanel and change the uploaded files named with the extension of ‘.txt’.
After you have completed all this—you can now proceed with the “Verify Domain” option on the punchsalad page. The verification will take anywhere between 30 seconds to a minute. You will see an option like this:
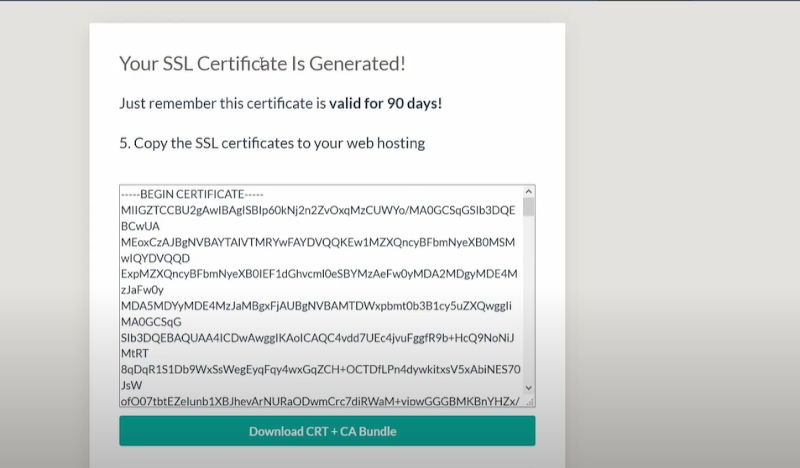
After you have completed the verification it means that you can install it in GoDaddy. Remember, that this certificate is just for 90 days after which you have to go through the entire process again.
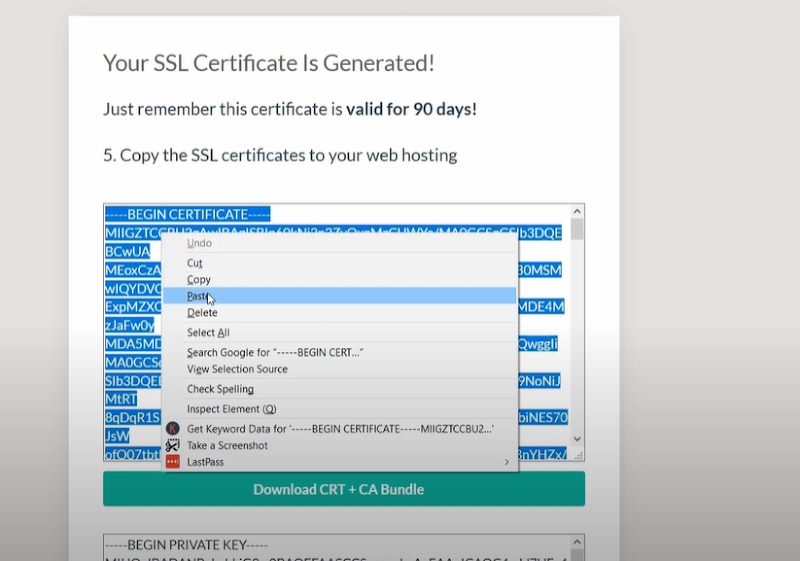
- Download all the files. After downloading copy the certificate and proceed to cPanel.
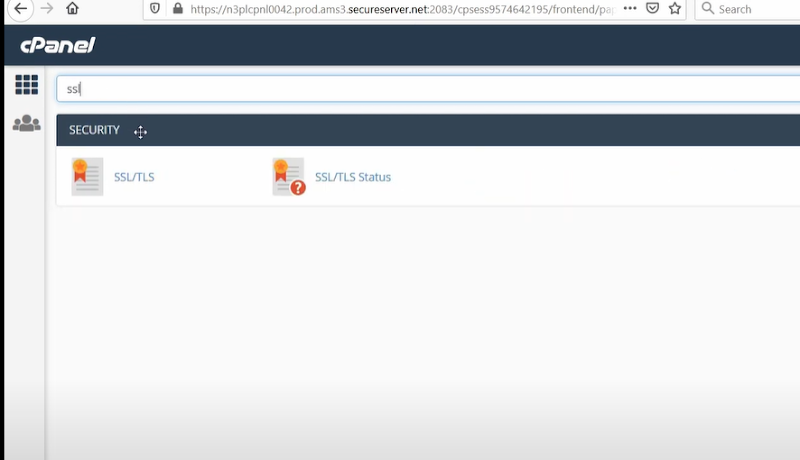
And, make a search for SSL
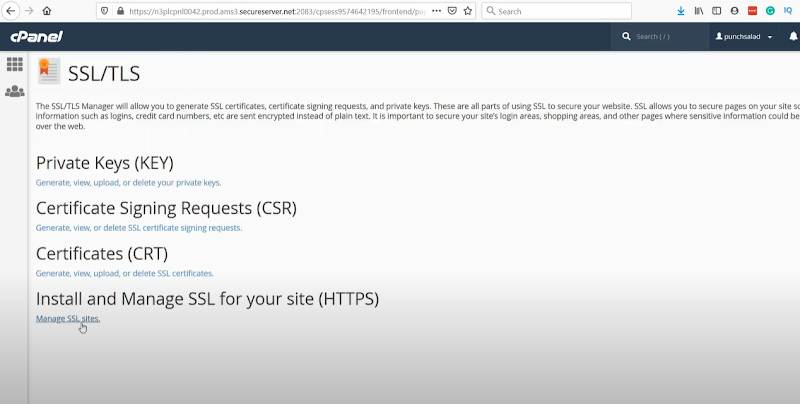
Selecting which you have to choose the fourth option saying: Manage SSL sites
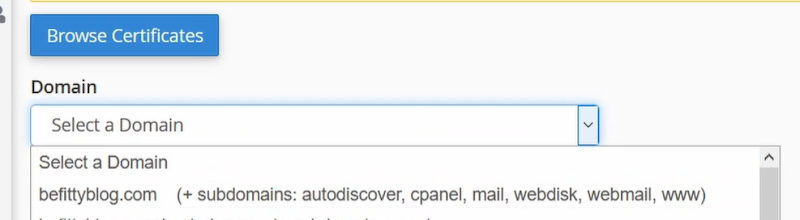
After selecting, Scroll Down to the bottom of the page—where you have to select your domain.
After you have selected the domain—you have pasted the certificate and private key in the boxes.
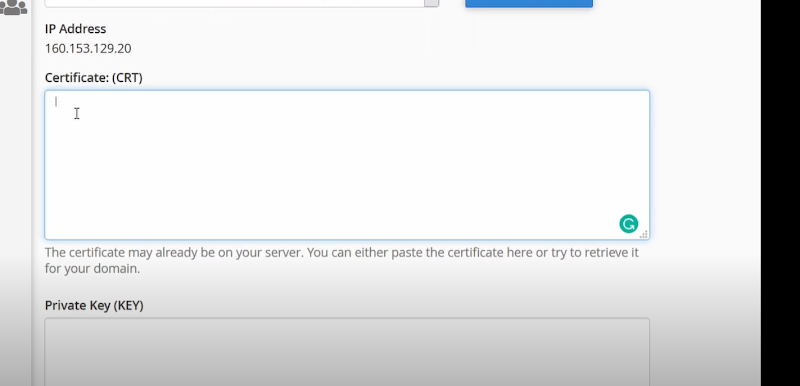
After pasting you will notice that there are two certificated in one—so you have to cut the additional certificate.
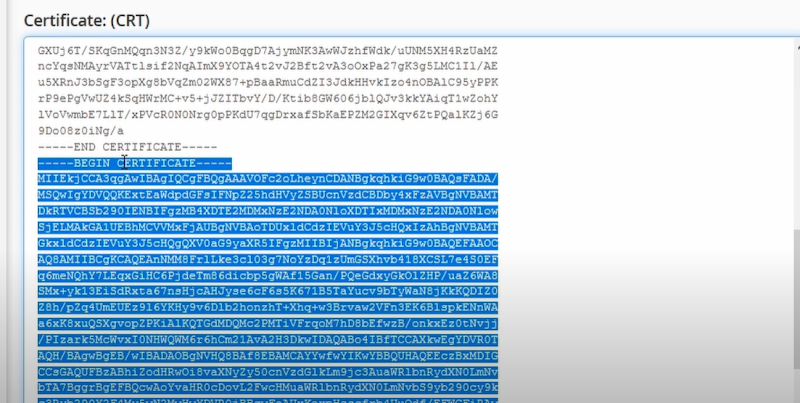
After that scroll down and paste the certificate which you have removed, in the ‘certificate authority bundle’ box.
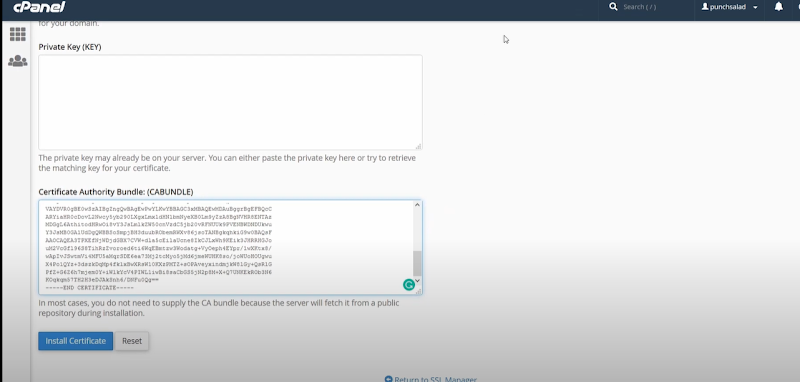
- Similarly, copy the private key from punchsalad and paste it in the column of the private key.
If you have done something wrong—you will get an error report right next to the boxes if you have followed the steps correctly—there will be no such errors. However, you can correct them by repeating this process.
- After you have done this, select the option of “Install Certificates”. After a few seconds, you will get a confirmation which says: successfully install.
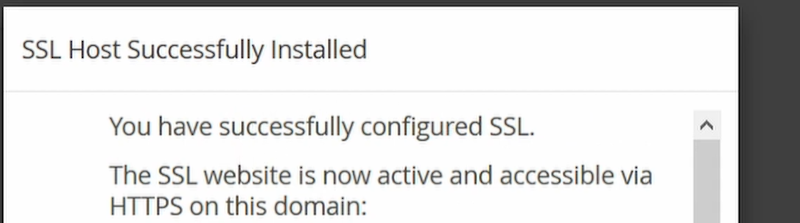
After you have completed this—click ok.
Now, go to your website and in the search bar—where you see the un-secure option: Choose and add the ‘https://’ before your domain name and reload the page. You will see that the free SSL certificate is successfully installed and your website is secured. However, for a period of 90 days only, upon which you will have to go through the whole process again.
Additional Information: This process is necessary.
Your website is now secured and has an SSL certification—but the people who will come with ‘http://’ instead of https:// to your website—Google will show them the option of ‘unsecured connection’. To avoid this, go to your GoDaddy cPanel.
And under folder public _html (the same we used before). You will see an option of ‘.htaccess’. If you do not just create a file named “.htaccess”. Most of the time—this file is hidden which you have un-check as earlier discussed.
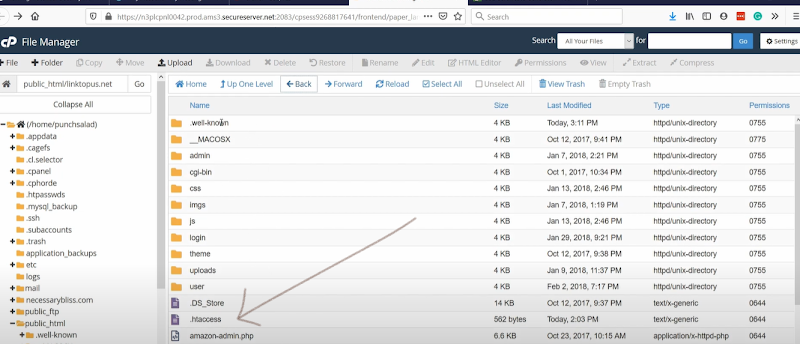
Right-clicking it—you will see the option of the edit.
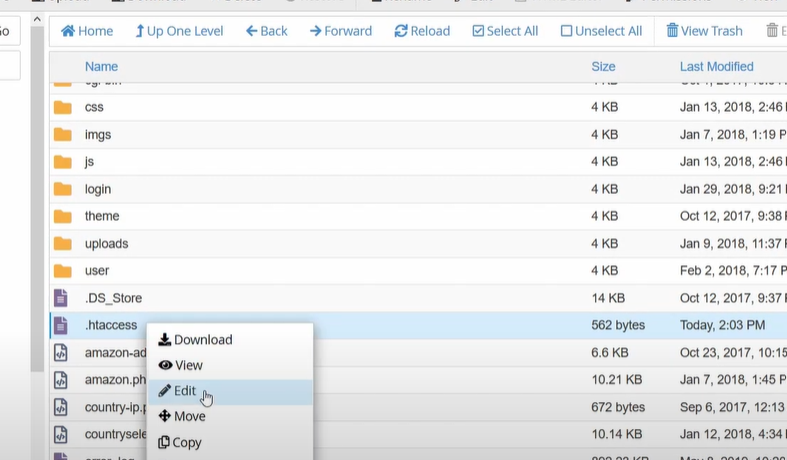
Click on edit and then select the ‘Edit’ option on the pop-up box.
You will be redirected to a new window where you will see a code like this:
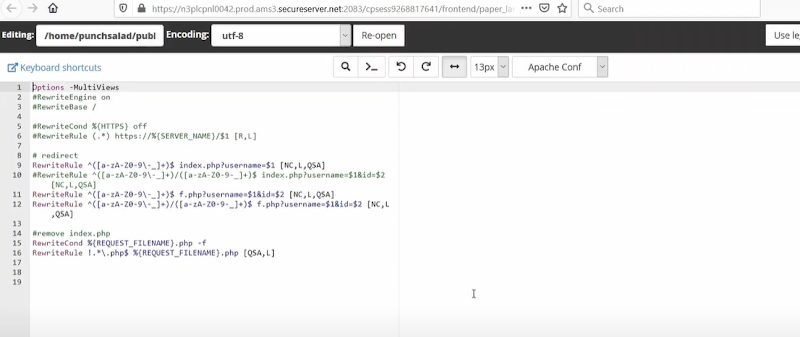
Do not edit anything, instead, at the bottom paste the code given below.
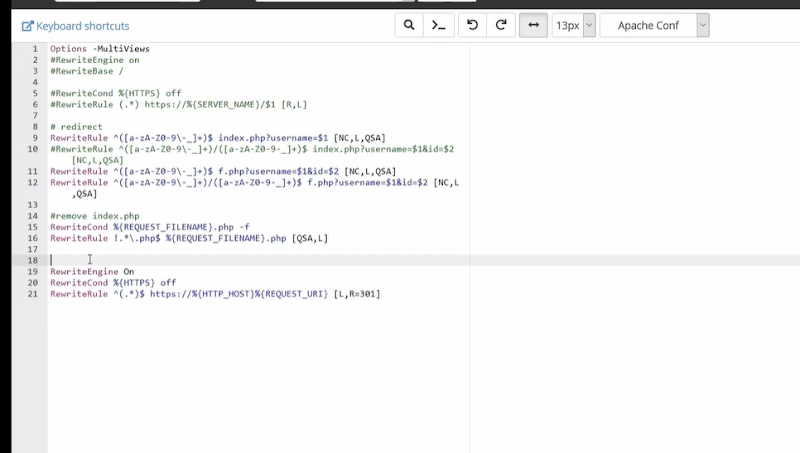
The Code is :
| RewriteEngine On RewriteCond %{HTTPS} off RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [L,R=301] |
After this: Click on the “Save Changes” option at the right-uppermost corner.
Now, if anyone comes to your website from http:// or http:// —Google will show that your website is secured.
It means that your customers will be happy that your website is completely safe to use and share information.
Let’sencrypt is really a great free SSL certificate provider—but the process of repeating it every 90 days is quite worrisome to many as people forget and going through all these again can be hectic and inconvenient. If that is the case, you can go with other options of cheap SSL certificate providers.
Related article: Website Speed Optimization

